Update
One Health
The recent pandemic has reminded us of the deep connections between health and the environment. Adopting a One Health approach is critical not only to prevent outbreaks in zoonotic diseases, but also other urgent environmental issues including food safety and antimicrobial resistance. This page aims at listing the latest information, research, data and/or press releases issued by our partners in Geneva and other institutions around the world.
One Health Approach
One Health is an approach in which multiple sectors work together to achieve better public health outcomes (WHO, 2017). It is rooted in the recognition that human health and animal health are interdependent and bound to the health of the ecosystems in which they exist (WOAH, n.d.). The complex nature of the interactions between people, animals and plants renders this collaborative, multisectoral and transdisciplinary approach critical to addressing future health risks and challenges.
The One Health High Level Expert Panel (OHHLE) – the advisory panel convened by World Health Organization (WHO), Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO), World Organization for Animal Health (WOAH, formely known as OIE) and United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) – has recently elaborated a new operational definition of One Health.
One Health is an integrated, unifying approach that aims to sustainably balance and optimize the health of people, animals and ecosystems. It recognizes the health of humans, domestic and wild animals, plants, and the wider environment (including ecosystems) are closely linked and inter-dependent.
The approach mobilizes multiple sectors, disciplines and communities at varying levels of society to work together to foster well-being and tackle threats to health and ecosystems, while addressing the collective need for clean water, energy and air, safe and nutritious food, taking action on climate change, and contributing to sustainable development.
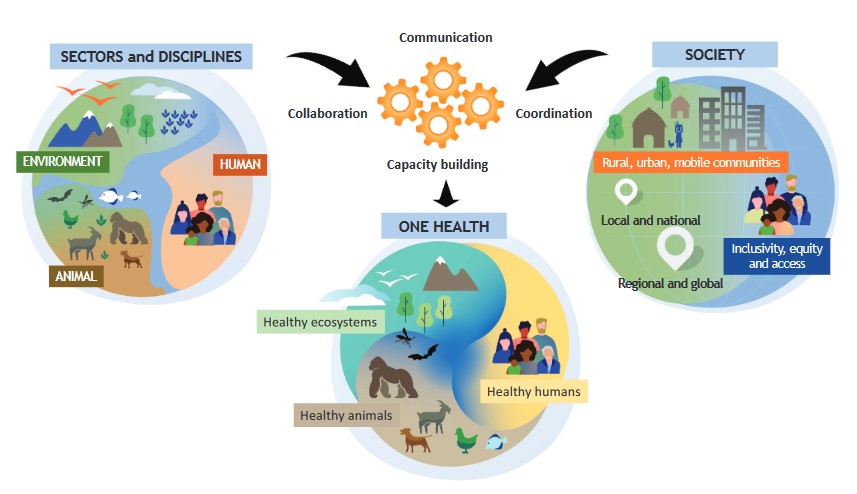
Illustration of the One Health approach by the OHHLEP
WHO, FAO, WOAH, and UNEP are working together to mainstream One Health so that they are better prepared to prevent, predict, detect, and respond to global health threats and promote sustainable development. At their first annual meeting as a quadripartite in March 2023, the partners launched a call to action for enhancing collaboration and cross-sector commitments to address global health emergencies. Priority actions all countries should undertake, include:
- Prioritize One Health in the international political agenda, increase understanding and advocate for the adoption and promotion of the enhanced intersectoral health governance;
- Strengthen national One Health policies, strategies and plans;
- Accelerate the implementation of One Health plans;
- Build intersectoral One Health workforces;
- Strengthen and sustain prevention of pandemics and health threats at sourc;
- Encourage and strengthen One Health scientific knowledge and evidence creation and exchange; and
- Increase investment and financing of One Health strategies and plans.
To fulfil its coordination and promotion role, the Quadripartite announced a One Health Joint Action Plan implementation guide, to be released in 2023.
Other institutions also provide useful resources to understand the One Health approach and its value for improving health.
- WHO: One Health | One Health in the WHO European Region | Newsletter
- FAO: One Health | Strategic Action Plan (2011)
- WOAH: One Health
- What is One Health | One Health Commission
- One Health | Swiss Tropical and Public Health Institute
- One Health | Biovision
- Quadripartite One Health Intelligence Scoping Study | Quadripartitie Alliance on One Health | November 2023
- WHO urges investing in “One Health” actions for better health of the people and the planet | 3 November 2023
- The Quadripartite Alliance and One Health | Inger Andersen | 27 March 2023
- Achieving health for all requires action on the economic and commercial determinants of health | Tedros Adhanom Ghebreyesus | The Lancet | 23 March 2023
- The Lancet Series on One Health and Global Health Security | The Lancet | 19 January 2023
- One Health for the Future: Three Pathways Against Tomorrow’s Crises | Foraus | August 2022
- Health in the Global Environmental Agenda: A policy guide | IISD | 20 January 2022
- Safeguarding Animal, Human and Ecosystem Health: One Health at the World Bank | The World Bank | 9 July 2020
- ‘One Health’- A Multi-dimensional Approach to Health | Public Health Notes | 23 November 2019
- Integrated approaches to health – A handbook for the evaluation of One Health | Simon Rüegg et al. | 2018
International Cooperation
Collaboration is a central component of the One Health approach as it transcends thematic boundaries and calls for comprehensive responses on health issues. International institutions, in International Geneva and beyond, have established collaborative programs to achieve the common goal of protecting health. This section provides information on these efforts.
One Health at the UN Environment Assembly
The deep connections between ecosystem health and human health were on the agenda of the second segment of the fifth UN Environment Assembly (UNEA-5.2), held in February 2022 in Nairobi. The concluding Ministerial Declaration recognized the risk for future pandemics and other health risks if humanity doesn’t overhaul its patterns of interaction with nature by adopting a holistic approach such as One Health. In this context, a resolution on animal welfare calls on Member States to protect animals, protecting their habitats and meeting their welfare requirements (UNEP/EA5/L10/REV.1). Another resolution on biodiversity and health recognizes the importance of the One Health approach to address the impacts of environmental crises on global health (UNEP/EA5/L11/REV.1). It further calls on Member States to promote the sustainable use, conservation and restoration of biodiversity with a view to preventing current and future health risks, including disease outbreaks with epidemic and pandemic potential.
Pandemic Treaty and One Health
The fourth meeting of the Intergovernmental Negotiating Body (INB 4) was held from 27 February to 3 March 2023 to draft and negotiate a World Health Organization convention, agreement or other international instrument on pandemic prevention, preparedness and response (WHO CA+). WHO Member States negotiated the “zero draft” prepared by the INB Bureau, which includes the recognition of the One Health Approach. According to civil society organizations that participated in a consultation on the document’s earlier draft this month, the draft pandemic accord needs more emphasis on preventing pandemics at their source.
World Health Day 2023
7 April is World Health Day, a global health awareness day that draws attention to a health topic of concern to the world. Celebrated every year, it also marks the anniversary of the founding of the World Health Organization in 1948. On 7 April 2023 ̶ World Health Day ̶ the World Health Organization will observe its 75th birthday. WHO’s 75th anniversary year is an opportunity to look back at public health successes that have improved quality of life during the last seven decades. It is also an opportunity to motivate action to tackle the health challenges of today ̶ and tomorrow. Promoting One Health approaches is an important aspects in this regard.
World Health Day 2022 was celebrated under the theme Our Planet, Our Health. In the midst of a pandemic, a polluted planet, increasing diseases like cancer, asthma, heart disease, the celebration raised attention on the urgent actions needed to keep humans and the planet healthy and foster a movement to create societies focused on well-being.
Zoonoses and emerging diseases
Zoonoses – diseases or infections that are naturally transmissible from vertebrate animals to humans (WHO, 2020) – are one of the health risks where the deep interconnections of human, animal and environmental health are most visible. Around 60% of existing human infectious diseases are zoonotic and 75% of emerging infectious diseases (including Ebola, HIV, influenza, COVID-19) have an animal origin (WOAH, n.d.). Controlling zoonotic pathogens at their animal source is the most effective and economic way of protecting people (WOAH, n.d.).
Food Safety
Food is another crucial theme to which the One Health approach can bring meaningful contributions. While food quality is a crucial component of human health, food production is highly reliable on animal and plant health. Moreover, many important zoonoses relate in some way to animals in the food production chain. Food is indeed an important vehicle for zoonotic pathogens, creating a deep bond between animal health on human health. The One Health approach is thus important for ensuring food safety. This section provides relevant resources in that area.
Antimicrobial Resistance
Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) occurs when microorganisms such as bacteria, viruses, fungi and parasites change in ways that render the medications used to cure the infections they cause ineffective (WHO, 2017). AMR is a global health concern as AMR infections cause 700’000 deaths each year and may become the leading cause of deaths globally by 2050 (UK O’Neill’s Commission, 2016). Although AMR occurs naturally, it is facilitated by the misuse and overuse of antibiotics in human health, food-animal production and agriculture, along with poor management of waste from households, farms, factories and healthcare settings (UNEP, n.d.). AMR depends greatly on the interaction between humans, animals and the environment, hence, adopting a One Health approach is critical for developing appropriate responses. This section presents the latest progress on addressing AMR through a One Health approach.
World Antimicrobial Awareness Week
World Antimicrobial Awareness Week (WAAW) is celebrated from 18-24 November every year. This year’s theme, Preventing Antimicrobial Resistance Together, is a reminder that antimicrobial resistance (AMR) is a threat to humans, animals, plants and the environment. The theme calls for collaboration across sectors through a One Health approach to to encourage the prudent use of antimicrobials and to strengthen preventive measures addressing AMR.
Biodiversity and Conservation
All human health ultimately depends on ecosystem services that are made possible by biodiversity and the products derived from them. Indeed, functioning ecosystems provide us with food and fresh water, aids in regulating climate, floods and disease, and provides recreational benefits (CBD, 2020). Investigating the complex interlinkages between biodiversity, ecosystem services and human health is thus essential to comprehensively address risks to human health. This section provides information on the application of the One Health approach in the field of biodiversity and conservation.
Climate Change
Global warming poses a growing threat to human health, as it impacts many vital elements of our lives such as air quality, access to drinking water, food security and the safety of our homes. Between 2030 and 2050, climate change is expected to cause approximately 250 000 additional deaths per year, from malnutrition, malaria, diarrhea and heat stress (WHO, 2018). Raising temperatures linked to climate change also contribute to animal migrations and offer favorable conditions for disease emergence and spread. Climate mitigation and adaptation is thus essential to decreasing health risks for both our generation and future generations. More information on health and climate change is provided in this section.
The Role of Geneva
Organizations are listed in alphabetical order.
Convention on Biological Diversity
The Convention on Biological Diversity facilitates awareness of biodiversity and health linkages and works closely with its partners, including UNEP, FAO, WOAH and WHO as well as other multilateral environmental agreements, with a view to contributing to those ongoing initiatives and promoting a biodiversity-inclusive One Health approach. The Secretariat of the Convention on Biological Diversity is also a member of the newly-established WHO-IUCN Expert Working Group on Biodiversity, Climate, One Health and Nature-based Solutions, established in March 2021. At its tenth meeting in 2010, the Conference of the Parties (COP) adopted the Strategic Plan for Biodiversity 2011-2020 with 20 global targets (Aichi Biodiversity Targets). In decision XII/21, the COP recognized the value of the “One Health” approach to address the cross-cutting issue of biodiversity and human health, as an integrated approach consistent with the ecosystem approach (decision V/6) that integrates the complex relationships between humans, microorganisms, animals, plants, agriculture, wildlife and the environment.
Food and Agriculture Organization Geneva Office
FAO promotes a One Health approach as part of the agrifood system transformation for the health of people, animals, plants and the environment. Ensuring a One Health approach is essential for progress to anticipate, prevent, detect and control diseases that spread between animals and humans, tackle AMR, ensure food safety, prevent environment-related human and animal health threats, as well as combatting many other challenges. A One Health approach is also critical for achieving the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).
FAO works with partners to promote health systemically, in particular, the Quadripartite which includes FAO, UNEP, WHO and WOAH. FAO focuses on eliminating hunger, promoting food security, food safety and healthy diets, preventing and controlling transboundary diseases, zoonoses and AMR, to protect the livelihoods of farmers from the impacts of plant and animal diseases, and to increase the sustainability and resilience of agrifood systems, with One Health benefits. FAO’s Joint Centre for Zoonotic Diseases and Antimicrobial Resistance coordinates One Health across different FAO divisions to mainstream One Health in FAO activities.
foraus
foraus is the Swiss participatory think tank on foreign policy. foraus conducted the “One Health” for the future project from November 2021 to December 2022, exploring zoonoses, antimicrobial resistance (AMR), and food safety and security threats, three major public health challenges which “One Health” aims at preventing and addressing. The project resulted into recommendations for necessary policy steps to be taken at national and international levels together with practitioners and experts from the field and a policy brief.
Health Diplomacy Alliance
The Health Diplomacy Alliance aims at advance health initiatives through diplomatic channels and foster collaborations and cooperation among local, national, and international stakeholders to address complex health challenges while emphasizing inclusivity, equity, and sustainable solutions.
Rosa-Luxemburg-Stiftung Geneva Office
The Rosa-Luxemburg-Stiftung Geneva Office works on social rights, socio-ecological transformation and the international organization of workers through conferences, seminars, workshops publications, studies or reports. This include work on the One Health Approach, envisaged by RLS as “an open and inclusive process, outside of usual thinking patterns and existing multilateral processes.” Relevant publications include: “One Health for the Future: Three Pathways Against Tomorrow’s Crises” (2022) in collaboration with Foraus.
United Nations Environment Programme
The United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) joined the One Health Quadripartite in 2022 as most of its work already mainstreamed the One Health principles through the coherent implementation of the environmental dimension of sustainable development within the UN system, and serving as an authoritative advocate for the global environment. Pursuing its mandate of preserving the health of the environment, UNEP contributes to fostering the health and well-being of humans, animals and plants.
World Organization for Animal Health
The World Organization for Animal Health (WOAH, founded as OIE) is global authority on animal health. WOAH brings its expertise in animal health and welfare to multisectoral partnerships aiming to develop global strategies to tackle major diseases or broader health threats, such as antimicrobial resistance. WOAH’s work promotes the One Health approach, recognizing the interdependence of animal, human and environmental health. Because the health of animals and of the environment strongly depend on human activities and our relationship with nature. Because the health of animals and the environment also determine human health. WOAH is part of the One Health Quadripartite with FAO, WHO and UNEP.
World Bank Group Geneva Office
The World Bank Group, including its Geneva Office, considers the One Health Approach a viable method to pursue its objectives of poverty eradication and boosting shared prosperity. Together with WHO, the World Bank co-convenes the Global Preparedness Monitoring Board (GPMB), an independent monitoring and accountability body, created in response to recommendations by the UN Secretary General’s Global Health Crises Task Force in 2017. World Bank recent publications on One Health include: Putting Pandemics Behind Us: Investing in One Health to Reduce Risks of Emerging Infectious Diseases (2022); One health: operational framework for strengthening human, animal, and environmental public health systems at their interface (2018).
Wolrd Health Organization
WHO integrates One Health across its units and offices, providing strategic advice relating to policy, and conducting training at the local, national and regional levels. WHO is a member of the One Health Quadripartite with FAO, WOAH and UNEP. Together, they have developed a One Health Joint Plan of Action that includes a set of activities that the 4 organizations can do together, including working with political leaders to establish the needed infrastructure and funding. WHO is the secretariat for the One Health High-Level Expert Panel (OHHLEP), which provides scientific advice to the Quadripartite partners on One Health priority setting, policies and strategies. This includes recommendations on good practice guidelines, a model One Health Surveillance System, a comprehensive list of upstream drivers of zoonotic disease spillover and recommendations to mitigate these risks.
Local Geneva & Switzerland
Federal Food Safety and Veterinary Office (FSVO)
In Switzerland, the “One Health” sub-organization, is led by the Federal Food Safety and Veterinary Office (FSVO) steers and coordinates this interdisciplinary, multi-sectoral cooperation. It brings together all the relevant federal and cantonal offices and associations in the fields of human medicine, veterinary medicine and natural, environmental and food sciences. The One Health sub-organization aims to work together to create added value in terms of human and animal health, and to have a positive effect on the environment. The Swiss Federal Office of Public Health (FOPH), Federal Food Safety and Veterinary Office (FSVO), Federal Office for Agriculture (FOAG) and Federal Office for the Environment (FOEN). together with the Armed Forces Veterinary Service and the cantonal enforcement agencies, set up in 2017 the One Health Interdisciplinary Platform to strengthen cooperation between public health, animal health, agriculture and the environment.
Academic Institutions
Geneva Graduate Institute (IHEID)
The Geneva Graduate Insitute Global Health Centre is one a research centres focusing on global health governance. As part of its research projects, the Governing Pandemics Initiative tracks efforts to address the gaps in the global system for governing preparedness for and responses to pandemics. The Global Health Centre’s Governing Pandemics initiative is tracking efforts to address the gaps in the global system for governing preparedness for and responses to pandemic.
University of Geneva (UNIGE)
The interdisciplinary One Health Unit (OHU) of the University of Geneva addresses emerging issues in Global Health at the human-animal-ecosystem interface, including both health risks resulting from human-animal interactions such as zoonosis but also opportunities for health promotion associated to biodiversity conservation. This brings together theory and practice from a diversity of fields such as epidemiology of infectious diseases, veterinary public health, environmental health, zoology and disease ecology, urban ecology, conservation sciences, and citizen cyber-science. The OHU leads innovative teaching activities (e.g. MOOC, flipped‐classroom, distance education in Kenyan refugee camp) and interdisciplinary research (e.g. impact of snakebite on humans and animals in Cameroon and Nepal) in collaboration with local, national and international partners (University Hospitals of Geneva, Citizen Cyberlab, InZone, WHO, MSF, ITU, EPFL, Swiss TPH, Institut Pasteur, University of Montreal). The OHU promotes an integrated One Health approach and digital innovation to better understand and tackle global health challenges at the interface of human, animal and environmental health.
Swiss Tropical and Public Health Institute
The Swiss Tropical and Public Health Institute (Swiss TPH) is a world-leading institute in global health with a particular focus on low- and middle-income countries. Its One Health group develops theoretical and methodological foundations for integrated human and animal health approaches.
Learning
- Global Health at the Human-Animal-Ecosystem Interface | University of Geneva, Institute Pasteur, University of Montreal and Centre Virchow-Villermé/University Paris Descartes
- One Health: Connecting Humans, Animals and the Environment | Swiss Tropical and Public Health Institute & University of Basel
- Bats, Ducks, and Pandemics: An Introduction to One Health Policy | Princeton University
- Online training on navigating the Tripartite Zoonoses Guide (TZG) | FAO, OIE & WHO
- Brochures, Infographics and Educational Material | One Health Commission
GEN Events

Nothing will happen without communities: The role of NGOs in strengthening environmental health
Geneva Health Forum 2022 | 4 May 2022

Nature-based Solutions and Health
Geneva Nature-based Solutions Dialogues | 26 April 2021

Emerging Infectious Diseases and Ecosystems Health
GENeva Environment Dialogues | 3 June 2022


